Understanding Sales Cycles sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with american high school hip style and brimming with originality from the outset.
Dive into the world of sales cycles, where knowing the ins and outs can make or break a business’s success.
Importance of Sales Cycles
Understanding sales cycles is crucial for businesses as it allows them to anticipate trends, plan resources effectively, and maximize revenue opportunities. By analyzing sales cycles, companies can identify peak seasons, slow periods, and consumer behavior patterns, enabling them to adjust their strategies accordingly.
Impact on Revenue and Profitability
- Knowing sales cycles can help businesses capitalize on high-demand periods, leading to increased sales and revenue.
- Anticipating slow seasons allows companies to manage inventory levels, reduce costs, and avoid overstock situations that can impact profitability.
- Analyzing sales cycles can also help businesses identify opportunities for cross-selling or upselling products/services, further boosting revenue.
Variation Across Industries
- Retail industry: Sales cycles in retail are often influenced by seasonal trends, holidays, and promotional events, impacting consumer buying behavior.
- Technology industry: Sales cycles in technology are driven by product innovation, upgrades, and consumer adoption rates, leading to frequent product launches and updates.
- Real estate industry: Sales cycles in real estate can be influenced by economic factors, interest rates, and market conditions, affecting property prices and transaction volumes.
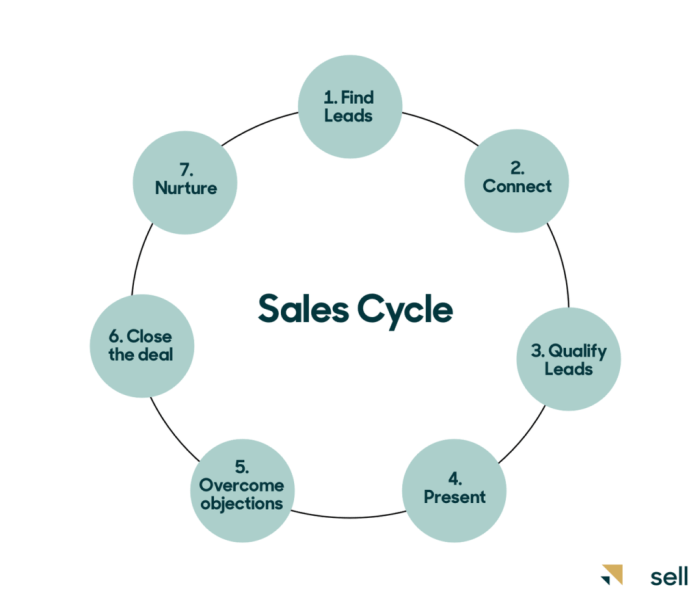
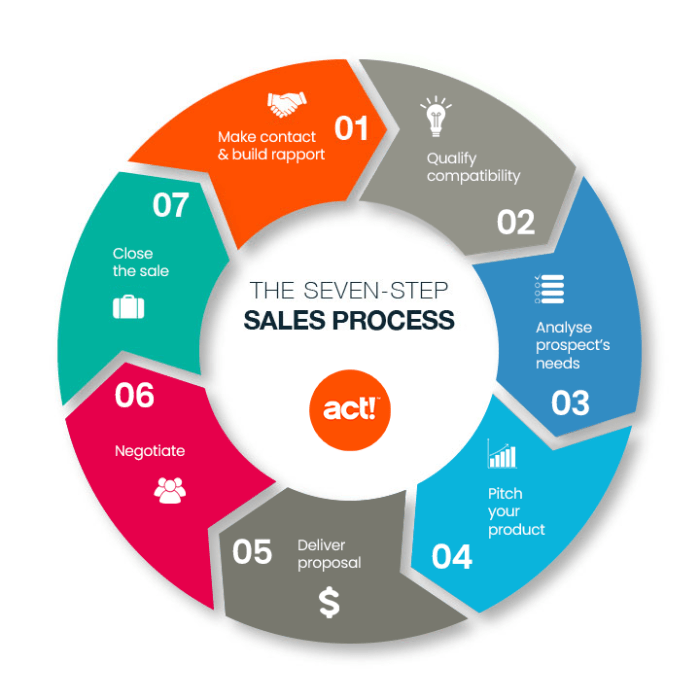
Phases of a Sales Cycle
In a sales cycle, there are several key phases that sales professionals go through from prospecting to closing a deal. Let’s dive into the typical stages and activities involved in each phase.
1. Prospecting
Prospecting is the first phase of the sales cycle, where sales reps identify potential leads or prospects. This involves researching and reaching out to individuals or companies who may be interested in the product or service being offered.
2. Qualification
During the qualification phase, sales reps evaluate the leads generated during prospecting to determine if they are a good fit for the product or service. This involves understanding the needs and budget of the prospect to ensure they are a qualified lead.
3. Needs Assessment, Understanding Sales Cycles
In this phase, sales reps work closely with the prospect to understand their specific requirements and pain points. By conducting a thorough needs assessment, sales professionals can tailor their pitch to address the prospect’s unique needs.
4. Presentation
Once the needs of the prospect are identified, sales reps move on to the presentation phase. This is where they showcase how their product or service can solve the prospect’s problems and add value to their business.
5. Handling Objections
During the sales cycle, it is common for prospects to raise objections or concerns. Sales reps must address these objections effectively to move the deal forward. This phase involves overcoming objections and building trust with the prospect.
6. Closing
The final phase of the sales cycle is the closing phase, where the sales rep finalizes the deal and secures the sale. This involves negotiating terms, pricing, and ensuring the prospect is ready to commit to the purchase.
Short Sales Cycles vs. Long Sales Cycles
Short sales cycles typically involve a quicker turnaround from prospecting to closing, often seen in industries with lower-priced products or services. On the other hand, long sales cycles are common in industries with complex or high-ticket items, requiring more time and effort to close a deal. Short sales cycles can lead to faster revenue generation, while long sales cycles may result in larger deal sizes but require more patience and persistence from sales professionals.
Factors Influencing Sales Cycles
When it comes to sales cycles, various external and internal factors can significantly impact their length and complexity.
External Factors
- Market Trends: Fluctuations in the market can affect customer purchasing behavior, leading to longer or shorter sales cycles.
- Competitive Landscape: The presence of strong competitors can make the sales process more challenging and prolonged.
- Economic Conditions: Recessions or economic booms can influence the willingness of customers to make purchasing decisions, directly impacting sales cycles.
Internal Factors
- Team Efficiency: The effectiveness of the sales team in qualifying leads, nurturing relationships, and closing deals plays a crucial role in determining the speed of the sales cycle.
- Customer Engagement: Building strong relationships with customers through personalized interactions and effective communication can accelerate the sales process.
- Product Knowledge: A deep understanding of the product or service being offered can help sales reps address customer needs more efficiently, potentially shortening the sales cycle.
Market Conditions Influence
- Seasonality: Certain industries experience peak sales periods during specific times of the year, impacting the duration of sales cycles.
- Industry Regulations: Compliance requirements and industry-specific regulations can introduce additional steps in the sales process, elongating the cycle.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in technology can streamline sales processes, leading to shorter sales cycles in industries that adopt these advancements.
Strategies for Shortening Sales Cycles: Understanding Sales Cycles
In the fast-paced world of sales, speeding up the sales cycle can lead to increased efficiency and ultimately, more revenue. Here are some tactics to help you shorten sales cycles without sacrificing quality.
Utilize CRM Systems for Efficient Lead Management
Using Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems can help you track and manage leads more effectively. By automating tasks such as follow-ups and reminders, you can ensure that no potential sale falls through the cracks.
Implement Targeted Marketing Campaigns
Tailoring your marketing campaigns to specific customer segments can help you reach the right audience at the right time. By focusing your efforts on those most likely to convert, you can shorten the sales cycle significantly.
Offer Personalized Solutions
By understanding the unique needs of each prospect, you can tailor your sales pitch to address their specific pain points. This personalized approach can lead to quicker decision-making and faster conversions.
Utilize Sales Enablement Tools
Sales enablement tools such as email automation, chatbots, and virtual demos can help streamline the sales process. These tools can provide valuable information to prospects and help move them through the sales funnel more efficiently.
Provide Quick Responses and Follow-ups
Timely responses to inquiries and prompt follow-ups after meetings or demos can keep prospects engaged and moving through the sales cycle. By being proactive and responsive, you can shorten the overall sales process.
Role of Technology in Streamlining Sales Cycles
Technology plays a crucial role in streamlining sales cycles by automating repetitive tasks, providing valuable insights through data analytics, and enabling better communication with prospects. Embracing the right technology tools can help accelerate the sales process and drive better results.












