Building a Marketing Research Process sets the stage for strategic decision-making and impactful business outcomes. Dive into the world of structured research methodologies and unlock the secrets to effective marketing strategies.
From defining research objectives to interpreting data findings, this journey will equip you with the tools to navigate the complex landscape of marketing research with confidence and finesse.
Introduction to Marketing Research Process
Marketing research is a crucial component for businesses looking to make informed decisions and stay ahead of the competition. By establishing a structured marketing research process, organizations can gather valuable insights that drive strategic planning and help identify opportunities for growth.
Importance of Building a Structured Marketing Research Process
- Ensures systematic data collection and analysis
- Provides a framework for decision-making based on facts and evidence
- Helps in understanding market trends and consumer behavior
- Guides the development of effective marketing strategies
Role of Marketing Research in Decision-Making, Building a Marketing Research Process
- Assists in identifying market opportunities and potential threats
- Provides insights into customer preferences and needs
- Evaluates the effectiveness of current marketing campaigns
- Supports product development and innovation
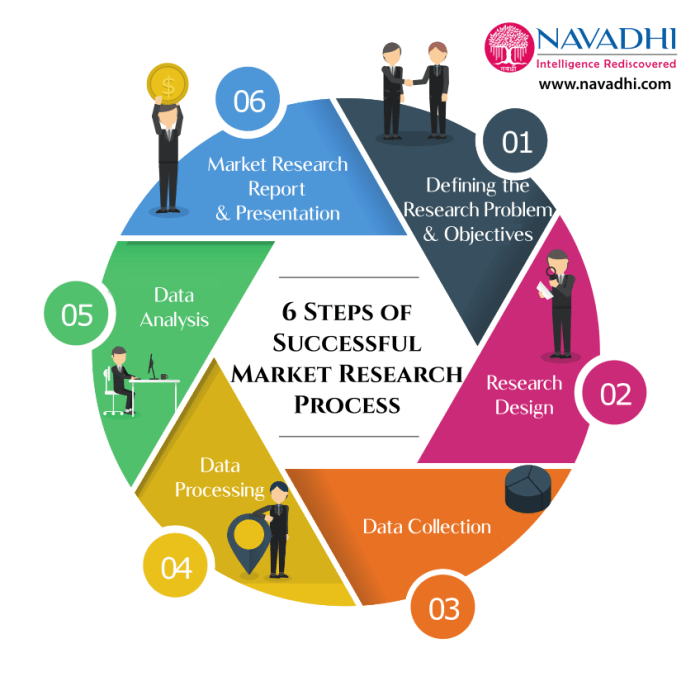
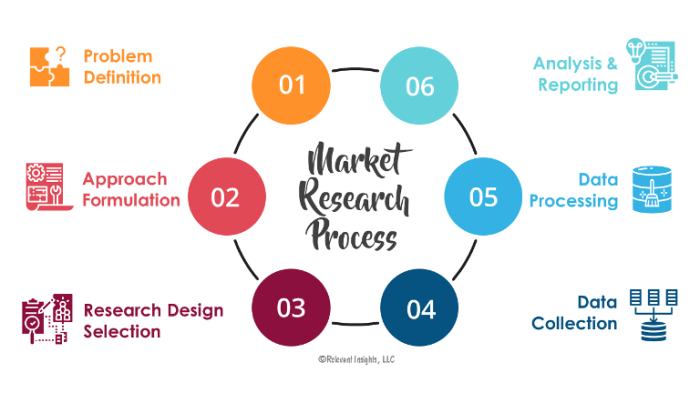
Key Components of a Marketing Research Process
- Defining the research problem and objectives
- Conducting a literature review
- Designing the research methodology
- Collecting and analyzing data
- Interpreting and presenting research findings
Setting Objectives and Scope
When embarking on a marketing research project, it is crucial to clearly define the research objectives and establish the scope of the study. This sets the foundation for the entire research process, guiding the team towards collecting the right data and analyzing it effectively.
Defining Clear Research Objectives
- Research objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- They should address the purpose of the research and what the team aims to achieve by the end of the study.
- Examples of clear research objectives include increasing brand awareness by 20% within six months, understanding consumer behavior towards a new product launch, or identifying market trends for a specific industry.
Significance of Establishing Scope
- Establishing the scope of the research helps in defining the boundaries of the study, ensuring that the team stays focused on the main objectives.
- It prevents the research from becoming too broad or too narrow, leading to irrelevant data collection and analysis.
- Scope also helps allocate resources efficiently and manage timelines effectively.
Examples of Specific Objectives
- For a product development research project: Identify customer needs and preferences to develop a new product that meets market demands.
- For a pricing strategy research project: Determine the optimal price point for a product to maximize profits while maintaining customer satisfaction.
- For a market segmentation research project: Divide the target market into distinct groups based on demographics, psychographics, and behaviors to tailor marketing strategies effectively.
Research Design and Methodology
Research design and methodology are crucial aspects of marketing research that determine the success of the study. It involves choosing the right approach to collect and analyze data, ensuring the results are valid and reliable.
Different Research Designs Suitable for Marketing Research
- Experimental Design: Involves manipulating variables to observe the effect on consumer behavior or preferences.
- Survey Design: Utilizes questionnaires or interviews to gather insights from target audiences.
- Observational Design: Involves observing and recording consumer behavior in real-world settings.
Importance of Selecting the Right Methodology for Data Collection
- Ensures accurate and relevant data is collected to address research objectives.
- Helps in minimizing bias and errors in data collection and analysis.
- Determines the validity and reliability of research findings.
Comparison of Quantitative and Qualitative Research Methods in Marketing Research
- Quantitative Research: Involves numerical data and statistical analysis to measure consumer behavior and preferences.
- Qualitative Research: Focuses on understanding consumer perceptions, motivations, and attitudes through open-ended responses and observations.
- Quantitative research provides measurable and numerical data for statistical analysis, while qualitative research offers in-depth insights into consumer behavior and preferences.
Data Collection Techniques
Data collection techniques are crucial in marketing research to gather information for analysis and decision-making. There are various methods used to collect data, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Let’s explore the primary and secondary data sources and when to use surveys, focus groups, interviews, and observation methods.
Primary Data Sources
- Advantages:
- First-hand information specific to the research objective.
- Control over data collection process and quality.
- Opportunity to customize questions for in-depth insights.
- Disadvantages:
- Time-consuming and costly to collect data directly.
- May require skilled researchers for accurate interpretation.
- Potential bias in responses due to interviewer or respondent factors.
Secondary Data Sources
- Advantages:
- Cost-effective and time-saving as data is readily available.
- Provides historical context and industry trends for analysis.
- Supplements primary data for a comprehensive research approach.
- Disadvantages:
- Data may not be specific or tailored to the research needs.
- Potential inconsistencies or inaccuracies in secondary sources.
- Risk of outdated or irrelevant information affecting research validity.
Surveys
Surveys are a popular data collection method involving structured questionnaires distributed to a target audience to gather feedback on specific topics. They are ideal for large sample sizes and quantitative data analysis.
Focus Groups
Focus groups bring together a small group of individuals to discuss a particular topic under the guidance of a moderator. This method allows for in-depth qualitative insights through group interactions and discussions.
Interviews
Interviews involve direct one-on-one conversations between the researcher and participant, providing detailed and personal insights. They are suitable for exploring complex topics and understanding individual perspectives.
Observation Methods
Observation methods involve researchers observing and recording behavior, interactions, or events without direct interaction with participants. This approach is valuable for studying natural behavior in real-time settings.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
Data analysis is a crucial step in the marketing research process as it involves examining the collected data to uncover patterns, trends, and insights that can help make informed decisions. Once the data is collected through various techniques, it needs to be analyzed to extract meaningful information.
Analyzing Marketing Research Data
Before diving into data analysis, it is essential to clean and organize the data to ensure accuracy and reliability. Once the data is cleaned, statistical tools and techniques are used to analyze the data. This can include descriptive statistics, regression analysis, factor analysis, and more. By applying these methods, researchers can identify relationships, correlations, and trends within the data.
Interpreting Research Findings
Interpreting research findings involves making sense of the analyzed data and drawing conclusions based on the results. This process requires researchers to look for patterns, anomalies, and significant findings that can help answer research questions or objectives. Effective interpretation of research findings is crucial in translating data into actionable insights for decision-making.
Drawing Meaningful Conclusions
To draw meaningful conclusions from data analysis in the marketing context, researchers need to connect the findings back to the research objectives. By linking the analyzed data to the initial research questions, researchers can draw insights that are relevant and valuable for the business. This involves synthesizing the results, identifying key takeaways, and making recommendations based on the findings.
Reporting and Presentation of Findings: Building A Marketing Research Process
When it comes to sharing the results of your marketing research, a well-structured research report is key. This report should effectively communicate your findings, insights, and recommendations to stakeholders.
Structuring a Comprehensive Research Report
Creating a comprehensive research report involves organizing your findings in a logical manner. Start with an executive summary that highlights the key points, followed by an introduction, methodology, results, analysis, conclusions, and recommendations. Make sure to use clear headings and subheadings for easy navigation.
Importance of Clear and Concise Presentation
Presenting your findings in a clear and concise manner is crucial for ensuring that stakeholders can easily understand the information. Avoid jargon and technical language, and use simple language to convey complex ideas. Focus on the most important insights and findings to keep the report concise and to the point.
Creating Impactful Visual Representations
Visual representations such as charts, graphs, and infographics can help make your data more digestible and engaging for your audience. When creating visuals, keep them simple, relevant, and visually appealing. Use colors strategically to highlight important information, and provide clear labels and titles for easy interpretation.












