When it comes to Customer Acquisition Cost, get ready to dive into a world where businesses crunch numbers and strategize like pros. From calculating CAC to reducing it, this topic is all about making those marketing dollars count.
Let’s explore the ins and outs of CAC, from how businesses determine this crucial metric to the strategies they use to keep it low and maximize their ROI.
Definition of Customer Acquisition Cost
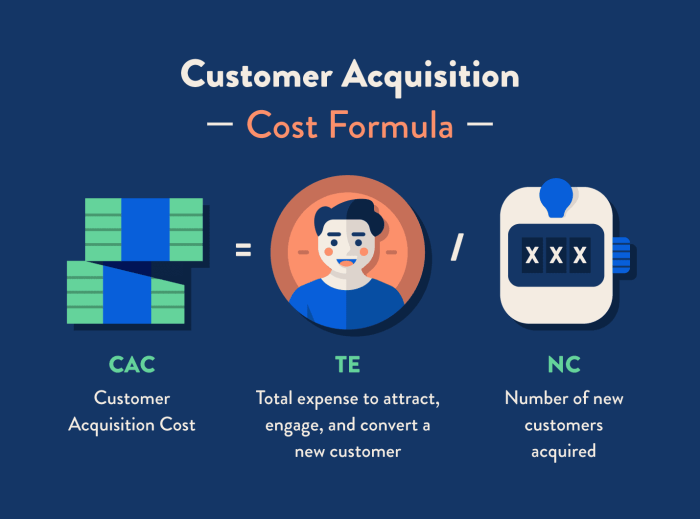
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is a crucial metric that helps businesses measure the cost involved in acquiring a new customer. It is essential for companies to understand their CAC to determine the effectiveness of their marketing and sales strategies and to ensure profitability.
Formula for Calculating Customer Acquisition Cost
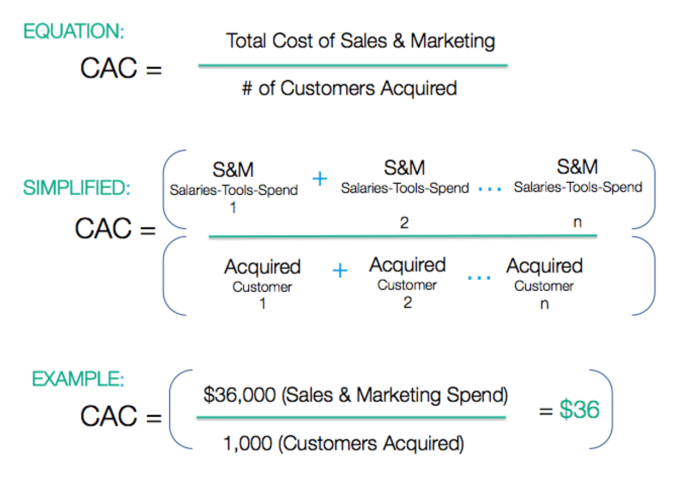
CAC = Total Sales and Marketing Expenses / Number of New Customers Acquired
- Identify all costs related to sales and marketing efforts.
- Divide the total expenses by the number of new customers acquired within a specific period.
- The resulting figure represents the average cost of acquiring a new customer.
Examples of Calculating and Interpreting CAC
Businesses across various industries calculate and interpret their CAC differently based on their specific goals and resources. Here are some examples:
| Company | Total Sales and Marketing Expenses | Number of New Customers Acquired | CAC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Company A | $10,000 | 100 | $100 |
| Company B | $20,000 | 50 | $400 |
In the examples above, Company A has a lower CAC compared to Company B, indicating that Company A is more efficient in acquiring new customers. This information can help businesses optimize their marketing strategies and allocate resources effectively.
Factors Influencing Customer Acquisition Cost
When it comes to Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC), several key factors can significantly impact how much a business spends to acquire new customers. Factors such as marketing channels, target audience, and industry type play a crucial role in determining the overall CAC.
Marketing Channels
The choice of marketing channels utilized by a business can greatly affect its CAC. Different channels have varying costs associated with them, and the effectiveness of each channel in reaching the target audience can impact the overall acquisition cost. For example, digital marketing channels like social media advertising may have lower costs compared to traditional print advertising, leading to a more optimized CAC for businesses that leverage these digital platforms effectively.
Target Audience
Understanding the target audience is essential in minimizing CAC. Businesses that have a clear understanding of their ideal customers can tailor their marketing strategies to reach them more effectively. By targeting the right audience segments, businesses can optimize their marketing efforts and reduce acquisition costs. For instance, conducting thorough market research and utilizing data analytics can help businesses identify high-value customer segments and focus their resources on acquiring those customers, ultimately lowering CAC.
Industry Type
The industry in which a business operates can also impact its CAC. Industries with high competition and saturated markets may require higher marketing spends to acquire customers compared to niche industries with less competition. Businesses operating in highly competitive industries may need to invest more in marketing and advertising to stand out from competitors and attract customers, leading to a higher CAC. On the other hand, businesses in niche industries may be able to acquire customers more cost-effectively due to lower competition and more targeted marketing efforts.
Strategies to Reduce Customer Acquisition Cost
Reducing Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is crucial for businesses to improve profitability and sustainability. By implementing effective strategies, companies can lower their CAC and enhance their overall marketing efficiency. One key aspect to consider in reducing CAC is the focus on customer retention, as retaining existing customers can significantly decrease the cost of acquiring new ones.
Importance of Customer Retention
Customer retention plays a vital role in reducing CAC, as it is generally more cost-effective to retain existing customers than to acquire new ones. By providing excellent customer service, personalized experiences, and loyalty programs, businesses can foster strong relationships with their customers and increase their lifetime value. This, in turn, can lead to lower CAC and higher overall profitability.
Real-Life Case Studies
1. Amazon Prime:
Amazon Prime is a prime example of a successful strategy in reducing CAC through customer retention. By offering a subscription-based service with exclusive benefits such as free shipping, streaming services, and discounts, Amazon has been able to increase customer loyalty and retention. This has led to a decrease in CAC as existing Prime members tend to make more frequent purchases and generate higher revenue for the company.
2. Starbucks Rewards Program:
Starbucks’ Rewards Program is another notable case study in reducing CAC through customer retention. By incentivizing customers with points for every purchase, offering personalized rewards, and exclusive offers, Starbucks has been able to retain a large customer base and drive repeat business. This has not only reduced CAC but also increased customer engagement and brand loyalty.
Calculating Return on Investment (ROI) based on Customer Acquisition Cost
In order to understand the effectiveness of their marketing efforts, businesses need to calculate the Return on Investment (ROI) based on the Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC). This metric helps companies determine how much revenue they are generating in comparison to the cost of acquiring new customers.
Relationship between CAC, Customer Lifetime Value (CLV), and ROI
Calculating ROI involves comparing the revenue generated from a customer with the cost of acquiring that customer. Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) is the total revenue a customer is expected to generate over their entire relationship with the business. By comparing CAC to CLV, companies can determine if they are spending an appropriate amount to acquire customers who will generate sufficient revenue to justify the cost.
- Businesses can calculate ROI using the following formula:
- For example, if a company’s CLV is $500 and their CAC is $100, the ROI would be calculated as follows:
- This means that for every $1 spent on customer acquisition, the company generates $4 in revenue.
ROI = (CLV – CAC) / CAC
ROI = ($500 – $100) / $100 = 4












