Understanding Customer Segmentation sets the stage for businesses to create tailored marketing strategies that resonate with specific customer segments, offering a deeper dive into the world of marketing dynamics.
Importance of Customer Segmentation
Customer segmentation refers to the process of dividing a broad target market into smaller, more specific groups of consumers who have similar characteristics, needs, or behaviors. This practice is crucial in marketing strategies as it allows businesses to tailor their products or services to meet the unique needs of different customer segments, ultimately leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Benefits of Understanding Customer Segments
- Improved Marketing Strategies: By understanding customer segments, businesses can create targeted marketing campaigns that resonate with specific groups, leading to higher conversion rates.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Tailoring products or services to meet the needs of different customer segments helps in providing a personalized experience, which can lead to increased customer loyalty.
- Increased Profitability: By focusing on high-value customer segments, businesses can optimize their resources and efforts, resulting in improved profitability.
Reasons to Invest in Customer Segmentation
- Effective Resource Allocation: Understanding customer segments helps businesses allocate resources efficiently by targeting the most profitable customer groups.
- Competitive Advantage: Businesses that effectively segment their customers gain a competitive edge by offering tailored solutions that meet specific customer needs.
- Market Expansion Opportunities: Customer segmentation can uncover new market segments or niches that businesses can target, leading to growth and expansion opportunities.
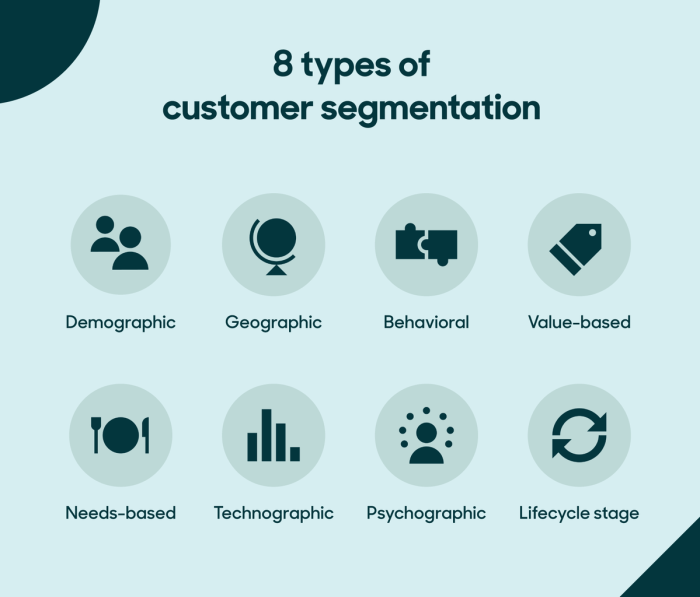
Types of Customer Segmentation
Customer segmentation can be done using various methods to understand different customer groups better. Let’s delve into the different types of customer segmentation methods and their effectiveness in different industries.
Demographic Segmentation
- Demographic segmentation divides customers based on factors like age, gender, income, education, occupation, and family size.
- Effective in industries like fashion, beauty, and healthcare where products and services are tailored to specific age groups or income levels.
- Example: Coca-Cola targets different age groups with their marketing campaigns, like Coke Zero for younger consumers and Diet Coke for older demographics.
- Challenges: Constantly changing demographics and the risk of stereotyping customers based on limited information.
Geographic Segmentation
- Geographic segmentation divides customers based on location, such as country, region, city, or climate.
- Effective in industries like tourism, real estate, and retail where consumer preferences vary by location.
- Example: Starbucks customizes store offerings based on the preferences of customers in different regions.
- Challenges: Balancing local preferences with global brand consistency and managing logistics for different locations.
Psychographic Segmentation
- Psychographic segmentation divides customers based on lifestyle, values, beliefs, attitudes, and interests.
- Effective in industries like luxury goods, travel, and entertainment where emotional connections drive purchases.
- Example: Apple targets customers who value innovation and design with their premium products.
- Challenges: Identifying and interpreting complex psychographic data accurately and ethically.
Behavioral Segmentation
- Behavioral segmentation divides customers based on their buying behavior, such as loyalty, usage rate, benefits sought, and occasion.
- Effective in industries like e-commerce, telecommunications, and FMCG where purchase patterns influence marketing strategies.
- Example: Amazon uses customer purchase history to recommend personalized products and offers.
- Challenges: Tracking and analyzing customer behavior accurately, especially in a digital environment.
Data Collection for Customer Segmentation: Understanding Customer Segmentation

Customer segmentation relies heavily on data collection to accurately divide customers into meaningful groups. Collecting data from various sources such as surveys, purchase history, social media, and website analytics is crucial in understanding customer behavior and preferences.
Sources of Data for Customer Segmentation
- Surveys: Gathering direct feedback from customers through surveys helps in understanding their needs and preferences.
- Purchase History: Analyzing past purchases provides insights into buying patterns and product interests.
- Social Media: Monitoring social media interactions helps in identifying customer sentiment and engagement with the brand.
- Website Analytics: Tracking website traffic, page views, and click-through rates can give valuable information on customer behavior online.
Importance of Data Quality and Accuracy
Data quality and accuracy are paramount in creating meaningful customer segments. Inaccurate data can lead to incorrect assumptions and ineffective segmentation strategies. It is crucial to ensure that the data collected is reliable, up-to-date, and relevant to the segmentation process.
Best Practices for Collecting and Organizing Data
- Define Clear Objectives: Clearly Artikel the goals of customer segmentation to guide data collection efforts.
- Use Multiple Data Sources: Combining data from various sources provides a comprehensive view of customer behavior.
- Regularly Update Data: Keep data up-to-date to ensure its relevance and accuracy in segmentation analysis.
- Utilize Data Management Tools: Implement tools and software to efficiently collect, organize, and analyze customer data.
Ethical Considerations in Data Collection
- Transparency: Inform customers about the data being collected and how it will be used for segmentation purposes.
- Data Security: Ensure that customer data is stored securely and protected from unauthorized access or misuse.
- Respect Privacy: Obtain consent before collecting any personal information and adhere to privacy regulations and guidelines.
Targeting Customer Segments
When it comes to targeting specific customer segments based on segmentation criteria, businesses need to analyze the characteristics and behaviors of each segment to tailor their marketing strategies accordingly. By understanding the unique needs and preferences of different customer groups, companies can create targeted campaigns that resonate with each segment.
Examples of Targeted Marketing Campaigns
- For example, a clothing retailer may target its younger customer segment with social media ads featuring trendy outfits and influencer collaborations, while focusing on email marketing promotions for its older, more traditional customer base.
- In another scenario, a fitness app might tailor its in-app messaging to encourage daily workout reminders for active users, while offering personalized nutrition plans to users who are more focused on weight management.
Role of Personalized Messaging and Product Offerings
- Personalized messaging plays a crucial role in targeting customer segments as it allows businesses to connect with customers on a more individual level, addressing their specific needs and preferences.
- By offering products and services that are tailored to each segment, companies can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty, ultimately driving sales and revenue.
Measuring Effectiveness of Targeting Strategies, Understanding Customer Segmentation
- Businesses can measure the effectiveness of their targeting strategies through metrics such as conversion rates, customer engagement, and sales growth within each segment.
- By analyzing these key performance indicators, companies can identify which strategies are working and which need adjustment, allowing them to optimize their targeting efforts for better results.












