Understanding GDPR Compliance sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with american high school hip style and brimming with originality from the outset.
Get ready to dive into the world of GDPR compliance and unravel the complexities surrounding data protection regulations in a cool and engaging way.
The Basics of GDPR Compliance
GDPR, which stands for General Data Protection Regulation, is a set of regulations designed to protect the personal data of individuals within the European Union. It has significant implications for businesses that handle personal data.
Main Principles of GDPR, Understanding GDPR Compliance
- Transparency: Individuals have the right to know how their data is being used.
- Consent: Companies must obtain explicit consent before collecting personal data.
- Data Minimization: Only collect data that is necessary for the intended purpose.
- Accuracy: Data must be accurate and kept up to date.
- Security: Measures must be in place to protect personal data from breaches.
Importance of GDPR Compliance for Businesses
- Avoid Fines: Non-compliance can result in hefty fines imposed by regulatory authorities.
- Enhance Trust: By ensuring data protection, businesses can build trust with their customers.
- Global Impact: GDPR compliance is not limited to EU businesses and affects any organization handling EU citizen data.
Key Elements of Personal Data under GDPR
- Identifiable Information: Any data that can directly or indirectly identify an individual.
- Sensitive Data: Information related to race, ethnicity, health, religion, etc., requiring special protection.
- Data Subject Rights: Individuals have rights to access, rectify, and erase their personal data under GDPR.
Understanding GDPR Requirements

GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) sets out specific requirements that organizations must follow to ensure the protection of personal data. This includes guidelines on data subject rights, obligations for data controllers and processors, and the importance of data protection impact assessments.
Core Requirements for GDPR Compliance
The core requirements for GDPR compliance include:
- Obtaining clear consent from individuals before processing their personal data.
- Ensuring data is collected for specified, legitimate purposes and not further processed in a manner incompatible with those purposes.
- Implementing appropriate security measures to protect personal data from unauthorized access, disclosure, alteration, or destruction.
- Maintaining accurate and up-to-date records of data processing activities.
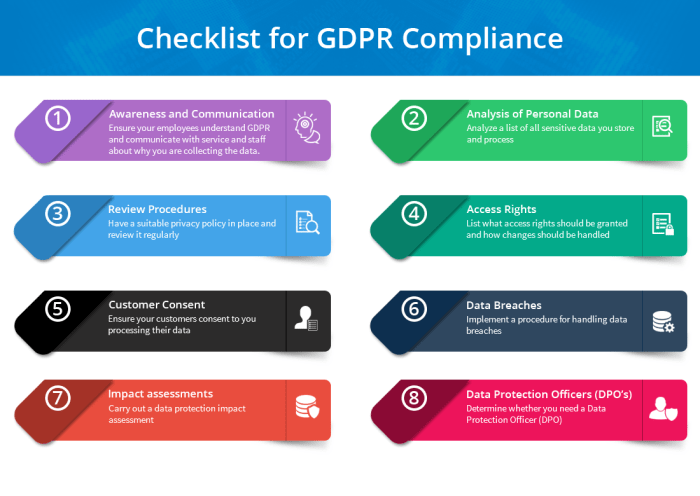
- Designating a Data Protection Officer (DPO) to oversee GDPR compliance.
Data Subject Rights under GDPR
Under GDPR, individuals have the following rights regarding their personal data:
- The right to access their personal data.
- The right to rectify inaccurate or incomplete data.
- The right to erasure of their data (also known as the “right to be forgotten”).
- The right to restrict or object to the processing of their data.
- The right to data portability, allowing them to obtain and reuse their personal data for their own purposes across different services.
Obligations for Data Controllers and Processors
Data controllers and processors have specific obligations under GDPR:
- Data controllers are responsible for ensuring compliance with GDPR principles and must only use processors that provide sufficient guarantees to implement appropriate technical and organizational measures.
- Data processors must only process personal data on documented instructions from the controller and assist the controller in fulfilling its obligations.
- Both controllers and processors must implement appropriate measures to ensure a level of security appropriate to the risk, including pseudonymization and encryption of personal data.
Importance of Data Protection Impact Assessments
Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs) are crucial under GDPR to identify and mitigate risks to individuals’ personal data. They help organizations assess the impact of data processing activities on data privacy and security, enabling them to implement measures to minimize risks and protect personal data effectively.
Implementing GDPR Compliance: Understanding GDPR Compliance
To achieve GDPR compliance, organizations must follow specific steps to ensure the protection of personal data and privacy rights of individuals.
Steps in Achieving GDPR Compliance
- Conduct a data audit to identify and categorize all personal data collected and processed.
- Update privacy policies and procedures to align with GDPR requirements.
- Implement security measures to protect data, including encryption and access controls.
- Obtain explicit consent from individuals for data processing activities.
- Train employees on GDPR regulations and best practices for handling personal data.
Tools and Software for GDPR Compliance
Some examples of tools and software that can help with GDPR compliance include data mapping tools, consent management platforms, and GDPR compliance software.
Role of a Data Protection Officer (DPO)
Having a Data Protection Officer (DPO) is crucial for ensuring compliance with GDPR. The DPO is responsible for overseeing data protection strategies, monitoring compliance efforts, and acting as a point of contact for data protection authorities.
Best Practices for Maintaining GDPR Compliance
- Regularly review and update data protection policies and procedures.
- Conduct periodic data protection impact assessments to identify and mitigate risks.
- Keep detailed records of data processing activities and consent management.
- Respond promptly to data subject requests and data breaches.
- Stay informed about changes in GDPR regulations and adjust practices accordingly.
GDPR Compliance Challenges and Solutions
Ensuring GDPR compliance can be a daunting task for organizations, as they face various challenges in meeting the requirements set forth by the regulation. Failure to comply with GDPR can have serious implications, including hefty fines and damage to reputation. However, there are strategies that organizations can implement to overcome these challenges and achieve successful GDPR compliance.
Common Challenges in GDPR Compliance
Organizations often struggle with the following challenges when trying to comply with GDPR:
- Lack of awareness about GDPR requirements
- Difficulty in managing and securing sensitive data
- Complexity in obtaining consent for data processing
- Ensuring data portability and the right to erasure
Implications of Non-Compliance with GDPR
Non-compliance with GDPR can lead to severe consequences, such as:
- Financial penalties of up to 4% of global annual turnover or €20 million, whichever is higher
- Loss of customer trust and damage to brand reputation
- Litigation and legal actions from data subjects
Strategies for Overcoming GDPR Compliance Challenges
Organizations can adopt the following strategies to address GDPR compliance challenges:
- Conducting regular training and awareness programs for employees
- Implementing robust data protection measures, such as encryption and access controls
- Developing clear policies and procedures for data processing and consent management
- Regularly auditing data processes and ensuring compliance with GDPR requirements
Successful GDPR Compliance Strategies
Some organizations have successfully achieved GDPR compliance by:
- Appointing a Data Protection Officer (DPO) to oversee compliance efforts
- Implementing Privacy by Design principles in product development
- Engaging with data subjects to ensure transparency and trust
- Regularly updating privacy policies and procedures to align with GDPR changes